What is the Difference Between Sanger Sequencing and Next Generation Sequencing?
Sanger Sequencing
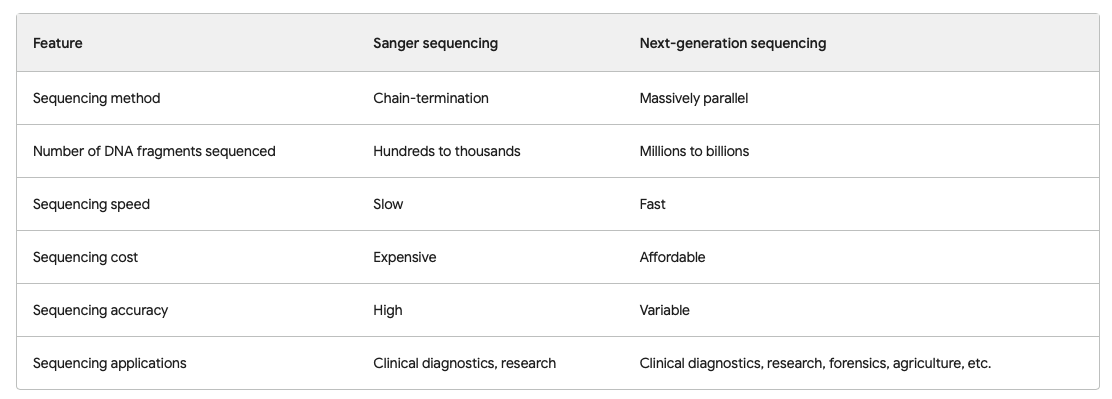
Sanger sequencing is a first-generation sequencing technology that was developed in the 1970s by Frederick Sanger. It is a chain-termination method that uses dideoxynucleotides to terminate DNA replication, resulting in DNA fragments of different lengths. The lengths of the fragments are determined by electrophoresis, and the sequence of the DNA is read from the resulting gel.
Sanger sequencing is a very accurate method for sequencing DNA. It is also a relatively slow method, and it can only sequence relatively short DNA fragments. Sanger sequencing is still the gold standard for sequencing small regions of DNA with high accuracy. However, it is not the best choice for sequencing large genomes or for applications where speed and cost are important.
Next Generation Sequencing
Next generation sequencing (NGS) is a second-generation sequencing technology that was developed in the early 2000s. It is a massively parallel method that sequences millions of DNA fragments simultaneously. NGS technologies use different methods to sequence DNA, but they all share the same goal of sequencing DNA more quickly and cheaply than Sanger sequencing.
NGS is a much faster method than Sanger sequencing, and it can sequence much larger DNA fragments. However, NGS is not as accurate as Sanger sequencing, and it can be more expensive. NGS is a good choice for sequencing large genomes or for applications where speed and cost are important.
How We Leverage Both Technologies
At PeploBio, we leverage both Sanger sequencing and NGS to provide our clients with the best possible sequencing services. We use Sanger sequencing for applications where accuracy is critical, such as clinical diagnostics. We use NGS for applications where speed and cost are important, such as research and forensics.
We are committed to providing our clients with the most accurate and affordable sequencing services possible. We are constantly evaluating new sequencing technologies, and we are always looking for ways to improve our services. If you are interested in learning more about our sequencing services, please contact us today.
Here are some additional details about the two technologies:
Sanger Sequencing
- Pros:
- Very accurate
- Relatively easy to use
- Can sequence small regions of DNA with high accuracy
- Cons:
- Slow
- Can only sequence relatively short DNA fragments
- Expensive
Next Generation Sequencing
- Pros:
- Fast
- Can sequence large genomes
- Relatively affordable
- Cons:
- Not as accurate as Sanger sequencing
- Can be more difficult to use
- Not as good for sequencing small regions of DNA
Conclusion
Sanger sequencing and next generation sequencing are both powerful tools for sequencing DNA. They have different strengths and weaknesses, and they are best suited for different applications. At PeploBio, we leverage both technologies to provide our clients with the best possible sequencing services.

